Topic-Specific Standards
Universal Standards
Universal Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-1 |
Process to determine material topics |
|
|
16 |
|
3-2 |
List its material topics |
A new material topic is business ethics. Resource efficiency and waste are covered by the topics of circular economy and resource efficiency, waste and plastic waste. Human rights now explicitly include labor rights; climate and energy is represented by the two topics of climate protection and adaptation to climate change. Employment and diversity now include inclusion and equality in the workplace. |
|
|
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
|
See topic-specific standards on material topics |
|
|
Economic
201: Economic Performance
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
201-1 |
Direct economic value generated and distributed |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Employees: Competition for talent |
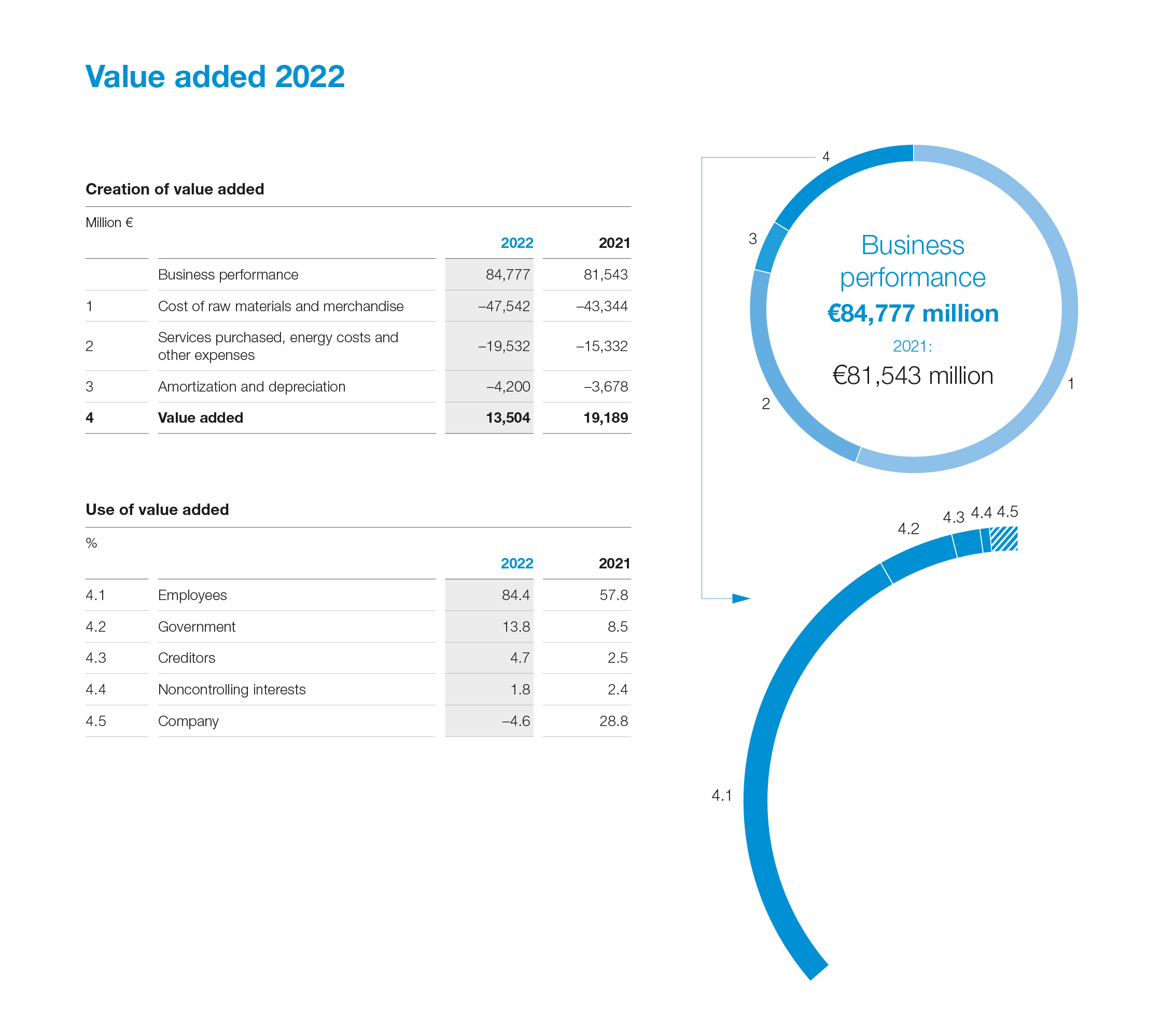
Graphic: Value added 2022 |
|
2, 5, 7, 8, 9 |
201-2 |
Financial implications and other risks and opportunities due to climate change |
Forecast: Opportunities and Risks: Operational opportunities and risks |
We report comprehensively on the results in the CPD climate change questionnaire. |
7 |
13 |
201-3 |
Defined benefit plan obligations and other retirement plans |
The BASF Group’s Business Year: Net Assets |
|
|
|
201-4 |
Financial assistance received from government |
|
The total amount of government grants cannot be determined on a global level; consequently, BASF refers to those government grants that were decisive for business decisions. In September 2022, BASF, SABIC and Linde started construction of the world’s first demonstration plant for large-scale electrically heated steam cracker furnaces. By using electricity from renewable sources instead of natural gas, the new technology has the potential to reduce CO2 emissions from one of the most energy-intensive production processes in the chemical industry by at least 90% compared to technologies commonly used today. |
|
|
202: Market Presence
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
202-1 |
Ratios of standard entry level wage by gender compared to local minimum wage |
|
The indicator is not industry-relevant. As an employer in the chemical industry, BASF typically recruits highly qualified employees. Their compensation is based on objective criteria worldwide, especially the employee’s position, their individual performance and BASF's success. |
6 |
1, 5, 8 |
202-2 |
Proportion of senior management hired from the local community |
|
The internationalization of its senior executives is an important factor for BASF as a global company, which is why we recruit across different countries and sites. |
6 |
8 |
203: Indirect Economic Impacts
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
203-1 |
Infrastructure investments and services supported |
Our Strategy: Our strategic action areas |
Graphic: Value added 2022 |
|
2, 5, 7, 9, 11 |
203-2 |
Significant indirect economic impacts |
Our Sustainability Concept: Our strategic approach |
|
|
1, 2, 3, 8, 10, 17 |
204: Procurement Practices
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
204-1 |
Proportion of spending on local suppliers |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Supplier management: Global procurement |
BASF does not have any specific guidelines for local procurement: In order to ensure local supply security, raw materials must be purchased where they are available around the globe. Local providers of technical goods and services often have competitive advantages due to their location. |
|
12 |
205: Anti-corruption
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
205-1 |
Operations assessed for risks related to corruption: |
Compliance: Monitoring adherence to our compliance principles |
Due to BASF's matrix structure, the number of the audited business sites is not a steering-relevant indicator. Group companies, which include several sites and business areas, are audited as part of compliance audits. Cross-business topics are also audited (e.g. donations and sponsorship). Our corporate audits focus on compliance issues. More than 25% of all audits performed under the risk-based annual audit plan are compliance audits. In addition, ad hoc audits are performed if there are grounds for suspicion. This regular auditing is an essential part of ensuring compliance worldwide in our business processes and identifying weaknesses or non-compliant behavior to derive appropriate measures. |
10 |
16 |
205-2 |
Communication and training about anti-corruption policies and procedures |
Compliance: Compliance Program and Code of Conduct |
All employees receive training on our Code of Conduct upon joining the company. They are obligated to attend refresher training every three years. |
10 |
16 |
205-3 |
Confirmed incidents of corruption and actions taken |
Compliance: Monitoring adherence to our compliance principles |
Compliance and responsible, forward-looking conduct are of central significance for BASF. According to our risk-based evaluation, we do not consider corruption a significant compliance risk. If individual cases of corruption are uncovered, these generally relate to passive corruption to the detriment of our company. Consequently, BASF does not report on cases of corruption unless they are considered material. There were no material cases of corruption in 2022. |
10 |
16 |
206: Anti-competitive Behavior 2016
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
206-1 |
Legal actions for anti-competitive behavior, anti-trust, and monopoly practices |
Consolidated Financial Statements: Notes: Risks from litigation and claims |
Any risks from litigation or claims are disclosed in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
|
16 |
Environmental
301: Materials
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
301-1 |
Materials used by weight or volume |
Due to the heterogeneity of our procurement portfolio, such an indicator (weight or volume) does not represent steering-relevant information. |
7, 8 |
8, 12 |
|
301-2 |
Recycled input materials used |
Material topics in focus: Circular Economy and Resource Efficiency |
We rely on our Verbund concept to make the most efficient use of raw materials in our own processes: Intelligently linking and steering our plants enables by-products from one facility to be used as feedstocks elsewhere and recirculated. This saves raw materials and energy. At the same time, the Verbund offers many opportunities to use renewable and recycled raw materials. We want to better leverage this potential and make it more measurable going forward. We have set ourselves two targets in our circular economy program: BASF has committed to converting 250,000 metric tons of recycled and waste-based raw materials to new products annually from 2025. By 2030, we want to increase our sales of solutions for the circular economy to €17 billion – double the 2020 figure. A percentage share of recycled feedstocks is not a relevant control indicator for us because this depends primarily on the market availability of these materials. |
8 |
8, 12 |
301-3 |
Reclaimed products and their packaging materials |
|
This indicator is not relevant to BASF’s product portfolio since most products are sold in bulk. The relevant legal regulations apply to the packaging used. In addition to the dual system for returning packaging for domestic goods, in Germany, for example, we organize the return and recycling of individual components of industrial and commercial packaging (plastics, steel, etc.) by recycling companies. We aim to offer our customers efficient disposal methods that are carried out professionally and responsibly for all packaging used. This is why we provide information about e.g. the companies that are available for returning and recycling industrial packaging. |
|
8, 12 |
302: Energy
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
302-1 |
Energy consumption within the organization |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Energy and Climate Protection: Energy supply |
Each site worldwide reports on environmental protection, safety, security and health protection in accordance with the reporting requirements defined in the Responsible Care Management System. |
7, 8 |
7, 12, 13 |
302-2 |
Energy consumption outside of the organization |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Energy and Climate Protection: Global targets |
Scope 3 emissions are described on the basis of the carbon footprint, which covers total energy consumption. |
8 |
7, 8, 12, 13 |
302-3 |
Energy intensity |
|
8 |
12, 13 |
|
302-4 |
Reduction of energy consumption |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Energy and Climate Protection: Strategy and Governance |
|
8, 9 |
8, 12, 13 |
302-5 |
Reductions in energy requirements of products and services |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Energy and Climate Protection: Strategy and Governance |
|
8, 9 |
8, 12, 13 |
303: Water and Effluents
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
303-1 2018 |
Interactions with water as a shared resource |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Our Management Systems: Responsible Care Management System |
Standards, methods and assumptions are defined in the reporting requirements in the Responsible Care Management System. |
|
|
303-2 2018 |
Management of water discharge-related impacts |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Our Management Systems: Responsible Care Management System |
Standards, methods and assumptions are defined in the reporting requirements in the Responsible Care Management System. |
|
|
303-3 2018 |
Water withdrawal |
Material topics in focus: Water: Graphic: Water in the BASF Group 2022 |
Standards, methods and assumptions are defined in the reporting requirements in the Responsible Care Management System. |
|
|
303-4 2018 |
Water discharge |
Material topics in focus: Water: Graphic: Water in the BASF Group 2022 |
Standards, methods and assumptions are defined in the reporting requirements in the Responsible Care Management System. |
|
|
303-5 2018 |
Water consumption |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Our Management Systems: Responsible Care Management System |
Standards, methods and assumptions are defined in the reporting requirements in the Responsible Care Management System and in the methodology paper. |
|
|
304: Biodiversity
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
7 |
14,15 |
304-1 |
Operational sites owned, leased, managed in, or adjacent to, protected areas and areas of high biodiversity value outside protected areas |
Proximity to protected areas is addressed on a location-by-location basis using the REHSA database. |
|
|
|
304-2 |
Significant impacts of activities, products, and services on biodiversity |
The impact of agricultural products, for example, is addressed as part of product development and portfolio assessment using the Sustainable Solution Steering method. |
|
|
|
304-3 |
Habitats protected or restored |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Raw Materials: Renewable resources |
|
8 |
6, 14, 15 |
304-4 |
IUCN Red List species and national conservation list species with habitats in areas affected by operations |
|
In the case of changes to the site portfolio, e.g. due to investments or acquisitions, we review the potential impacts as part of the standardized evaluation process. BASF also undertakes projects to protect individual species (skylark, monarch butterfly). We are testing the STAR tool for endangered species. |
|
|
305: Emissions
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
305-1 |
Direct (Scope 1) GHG emissions |
About this Report: Data |
|
7, 8 |
3, 12, 13, 14, 15 |
305-2 |
Energy indirect (Scope 2) GHG emissions |
About this Report: Data |
|
7, 8 |
3, 12, 13, 14, 15 |
305-3 |
Other indirect (Scope 3) GHG emissions |
|
7, 8 |
3, 12, 13, 14, 15 |
|
305-4 |
GHG emissions intensity |
|
8 |
3, 12, 13, 14, 15 |
|
305-5 |
Reduction of GHG emissions |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Energy and Climate Protection: Graphic: Schematic overview: Development of the BASF Group’s greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1 and 2) |
|
8, 9 |
3, 12, 13, 14, 15 |
305-6 |
Emissions of ozone-depleting substances (ODS) |
Material topics in focus: Emissions to Air, Waste and Remediation |
Calculation based on the substances described in the reporting requirements (based on the Montreal Protocol). |
7, 8 |
3, 12, 13 |
305-7 |
NOX, SOX and other significant emissions to air |
Material topics in focus: Emissions to Air, Waste and Remediation: Table: Emissions to air |
Calculation based on the methods described in the reporting requirements and includes CO, NOX, SOX, NMVOCs, PM, NH3 and other inorganic substances. |
7, 8 |
3, 12, 13 |
306: Waste (2020)
308: Supplier Environmental Assessment
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
308-1 |
New suppliers that were screened using environmental criteria |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Supplier Management: What we expect from our suppliers |
The requirements for our suppliers are defined in our Supplier Code of Conduct. Our suppliers must commit to complying with these requirements in the areas of environmental protection, human rights, labor and social standards, as well as fighting discrimination and corruption. In 2022, approximately 5400 suppliers of raw materials, technical goods, services and investment goods committed to these values in our registration portal. |
|
|
308-2 |
Negative environmental impacts in the supply chain and actions taken |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Supplier Management: What we expect from our suppliers |
One business relationship with suppliers was terminated due to severe deficiencies in the areas of environmental protection, safety, security and health protection, and social matters. 397 suppliers were asked for improvements in the areas of environmental protection, safety and security, and health protection, representing approximately 38% of all suppliers audited in 2022. |
|
|
Social
401: Employment
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
401-1 |
New employee hires and employee turnover |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Employees: Competition for talent |
We report the total number of new hires and the early turnover rate (within the first three years), both by region since these are our internal steering-relevant indicators. New employees are hired based on qualification and suitability; age is irrelevant. |
6 |
5, 8 |
401-2 |
Benefits provided to full-time employees that are not provided to temporary or part-time employees |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Employees: Compensation and benefits |
We hire few temporary employees worldwide. All types of benefits that we provide in Germany are available to both full-time and part-time employees. |
|
8 |
401-3 |
Parental leave |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Employees: Balancing personal and professional life |
Our employees can take parental leave in line with the relevant legal entitlements. In addition, BASF has defined a Group-wide standard for maternity protection to protect the health of expectant and nursing mothers and to prevent harm to them and their babies. This includes at least 14 weeks of maternity leave (no less than 6 weeks after delivery). Compliance with the internal maternity leave policy is evaluated and monitored as part of a global risk-based management process. In some countries, we thus provide a standard of maternity protection that goes beyond local statutory regulations. |
6 |
5, 8 |
402: Labor/Management Relations
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
402-1 |
Minimum notice periods regarding operational changes |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Employees: Mutual respect and open dialog |
Compliance with national laws is a cornerstone of our business; in many cases, we exceed statutory requirements. We also adhere to the applicable notice periods based on national laws or local collective agreements. |
3 |
8 |
403: Occupational Health and Safety
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
403-1 2018 |
Occupational health and safety management system |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Our Management Systems: Responsible Care Management System |
Our Responsible Care Management System contains occupational safety and health protection elements, which cover all employees and temporary employees of BASF and its contractors. Furthermore, 55% of all employees (BASF, temporary, contractors) are additionally covered by a local management system audited in accordance with ISO 45001/OHSAS 18001. |
|
3, 8 |
403-2 2018 |
Hazard identification, risk assessment, and incident investigation |
Material topics in focus: Occupational Safety, Process Safety and Health Protection: Occupational safety |
We encourage and promote a culture of safety where everyone is mindful of hazards and helps to resolve and avoid them by doing the right thing. A systematic process has been established for all routine tasks and workplaces to identify and assess potential hazards, to derive appropriate safety measures, and to ensure that these are implemented and effective. Separate hazard assessments are used to manage non-routine tasks as part of a separate approval process. |
|
3, 8 |
403-3 2018 |
Occupational health services |
We offer our employees a comprehensive range of medical services, from preventive occupational medicine and emergency care to health promotion. We do not offer this service to our contractors. BASF’s corporate health management has been established for all Group companies worldwide and serves to improve and promote the health and productivity of our employees. Worldwide standards for occupational health are specified in a binding Group-wide directive that is implemented by a global network of experts. We regularly review our performance, for example with occupational health audits. In addition, we have established an expanded indicator for our global health management: the Health Performance Index (HPI). |
|
3, 8 |
|
403-4 2018 |
Worker participation, consultation, and communication on occupational health and safety |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Our Management Systems: Responsible Care Management System |
We offer our employees around the world a large amount of information on various health topics in German and English. At all sites, employees can consult medical professionals as needed on health matters in the workplace. Appropriate committees on health and safety topics are established at the local level. BASF’s and leasing staff at all sites are involved in developing task-related risk assessments and establishing operating procedures. Contractors are involved in work authorization procedures to reduce interaction risks. |
|
3, 8 |
403-5 2018 |
Worker training on occupational health and safety |
In addition to the legally required briefings, BASF requires new employees and contractors to complete additional, compulsory health and safety training, as well as regular training on the safe handling of chemicals and the correct use of personal protective equipment for employees at our production sites.We train BASF employees and contractors/site partners as first aiders. First aid is one of five core elements of the Health Performance Index (HPI), which BASF uses to measure its performance in occupational medicine and health protection every year. All employees receive training before starting work and at regular intervals, and are tested to ensure that this training was understood. Training needs are based on an employee’s individual field of work and tasks, as well as the statutory requirements. |
|
3, 8 |
|
403-6 2018 |
Promotion of worker health |
BASF employees and managers have access to various offerings to maintain or improve their health through the global health promotion program. The program comprises three elements:
Health promotion is one of five core elements of the Health Performance Index (HPI), which BASF uses to measure its performance in occupational medicine and health protection every year. The program applies only to direct BASF employees. |
|
3, 8 |
|
403-7 2018 |
Prevention and mitigation of occupational health and safety impacts directly linked by business relationships |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Supplier management |
In general, BASF takes a preventative approach to occupational health and safety risks. This approach is based on the elements of the Responsible Care Management System and is likewise used by our contract manufacturers, and regularly audited by us. The safety and environmental performance of suppliers and contractors are considered during the procurement process. |
|
3, 8 |
403-8 2018 |
Workers covered by an occupational health and safety management system |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Our Management Systems: Responsible Care Management System |
The occupational health and safety elements of our Responsible Care Management System cover all BASF, temporary and contractors’ employees. The coverage by certified health and safety management system is explained in GRI 403-1. |
|
3, 8 |
403-9 2018 |
Work-related injuries |
Our aim is to avoid lost-time injuries. We investigate all incidents with major accident potential worldwide to determine the main causes, independent of the outcome of the actual incident. Using a wide range of data enables us to better identify necessary measures for continuous improvement and to assess their implementation/effectiveness. In general, BASF does not differentiate between employees (BASF, leasing or contractors), as there is no differentiation in our company health and safety management system. Further details of most events occurring are not considered relevant. For BASF, chemical-related incidents are considered most specific to our own operations and are therefore communicated in our report. |
|
3, 8 |
|
403-10 2018 |
Work-related ill health |
Our aim is to avoid work-related illness completely through appropriate prevention.
In the 2022 reporting year, 38 (2021: 36) work-related diseases were documented as recognized occupational diseases among our direct employees worldwide. Deaths from work-related recognized diseases are not reported to BASF Group. The main work-related recognized diseases are occupational asthma, hearing loss, skin disease, musculoskeletal disease and cancer. |
|
3, 8 |
|
404: Training and Education
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
404-1 |
Average hours of training per year per employee |
|
In 2022, each employee spent an average of 1.7 days on further training. |
6 |
4, 5, 8 |
404-2 |
Programs for upgrading employee skills and transition assistance programs |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Employees: What we expect from our leaders |
|
|
8 |
404-3 |
Percentage of employees receiving regular performance and career development reviews |
|
The BASF Group has a uniform system in place for conducting employee dialogs that applies to all employees, regardless of gender and employee type. |
6 |
5, 8 |
405: Diversity and Equal Opportunity
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
405-1 |
Diversity of governance bodies and employees |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Employees: Graphic: BASF Group employee age structure |
Promoting and valuing diversity across all hierarchical levels is an integral part of our strategy and is also embedded in our corporate values so that all employees are part of our team. Therefore, a different indicator for minorities is not a steering-relevant parameter for us. |
6 |
5, 8 |
405-2 |
Ratio of basic salary and remuneration of women to men |
|
Representative evaluations for BASF SE have shown that there are no systematic differences between compensation of female and male employees in comparable roles and with comparable qualifications. There is no global evaluation. |
6 |
5, 8, 10 |
406: Non-discrimination
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
406-1 |
Incidents of discrimination and corrective actions taken |
Material topics in focus: Responsibility for Human Rights, Labor and Social Standards: International labor and social standards |
Number of complaints and tip-offs received in 2022 on human rights: 151 (of which resolved in the reporting period: 135) |
6 |
5, 8, 16 |
407: Freedom of Association and Collective Bargaining
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
407-1 |
Operations and suppliers in which the right to freedom of association and collective bargaining may be at risk |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Supplier Management: What we expect from our suppliers |
We did not identify any deficiencies in the areas of freedom of association and collective bargaining with the suppliers audited in 2022. Our monitoring here covers our direct suppliers (Tier 1). High-risk countries are those countries with high ESG risks. |
3 |
8 |
408: Child Labor
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
408-1 |
Operations and suppliers at significant risk for incidents of child labor |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Supplier management: Audit results |
Again in 2022, none of our audits identified any instances of forced labor, child labor or dangerous work and overtime performed by persons under 18. |
5 |
8, 16 |
409: Forced or Compulsory Labor
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
409-1 |
Operations and suppliers at significant risk for incidents of forced or compulsory labor |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Supplier management: Audit results |
Again in 2022, none of our audits identified any instances of forced labor, child labor or dangerous work and overtime performed by persons under 18. |
4 |
8 |
410: Security Practices
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
410-1 |
Security personnel trained in human rights policies or procedures |
In accordance with our company guidelines, training on human rights policies is mandatory for both BASF and contractors’ employees at all BASF sites. |
1 |
16 |
|
411: Rights of Indigenous Peoples
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
411-1 |
Incidents of violations involving rights of indigenous peoples |
|
Our internal grievance mechanisms did not identify any (potential) violation of rights of indigenous communities. We operate in countries with indigenous peoples, both in our supply chain and in our own operations. We take this into account in our investment activities. |
1 |
2 |
413: Local Communities
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
413-1 |
Operations with local community engagement, impact assessments, and development programs |
Our Sustainability Concept: Our strategic approach |
As a general rule, assessments are performed for all Group companies (as for labor and social standards) or as part of standardized evaluation processes for all material investment processes. As part of the piloting of the VBA methodology, BASF currently does not publish any Value to Society results. |
1 |
|
413-2 |
Operations with significant actual and potential negative impacts on local communities |
Graphic: How We Create Value |
|
1 |
1, 2 |
414: Supplier Social Assessment
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
414-1 |
New suppliers that were screened using social criteria |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Supplier Management: What we expect from our suppliers |
The requirements for our suppliers are defined in our Supplier Code of Conduct. Our suppliers must commit to complying with these requirements in the areas of environmental protection, human rights, labor and social standards, as well as fighting discrimination and corruption. In 2022, approximately 5,400 suppliers of raw materials, technical goods, services and investment goods committed to these values in our registration portal. |
|
|
414-2 |
Negative social impacts in the supply chain and actions taken |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Supplier Management: What we expect from our suppliers |
One business relationship with suppliers was terminated due to severe deficiencies in the areas of environmental protection, safety, security and health protection, and social matters. 397 suppliers were asked for improvements in the areas of environmental protection, safety and security, and health protection, representing approximately 38% of all suppliers audited in 2022. |
|
|
415: Public Policy
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
415-1 |
Political contributions |
BASF does not support political parties financially or through donations in kind. Grants are subject to a maximum limit and comprehensive documentation requirements. |
10 |
16 |
|
416: Customer Health and Safety
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
3-3 |
Management of material topics |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Stakeholder Engagement |
|
|
|
416-1 |
Assessment of the health and safety impacts of product and service categories |
Our Sustainability Concept: Our strategic approach |
As a producing company, we focus on the evaluation of our products. Services are not relevant for a producing company. |
7 |
|
416-2 |
Incidents of non-compliance concerning the health and safety impacts of products and services |
Consolidated Financial Statements: Notes: Risks from litigation and claims |
Any risks from litigation or claims are disclosed in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
|
16 |
417: Marketing and Labeling
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
417-1 |
Requirements for product and service information and labeling |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Product Safety: Strategy and governance |
International and regional chemical regulations such as the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) or the CLP Regulation, to which BASF is subject, involve comprehensive labeling obligations. These include information on the safe handling and disposal of products. |
7 |
12, 16 |
417-2 |
Incidents of non-compliance concerning product and service information and labeling |
Consolidated Financial Statements: Notes: Risks from litigation and claims |
Any risks from litigation or claims are disclosed in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
|
16 |
417-3 |
Incidents of non-compliance concerning marketing communications |
|
Not a key indicator as BASF mainly operates in the B2B sector. Any risks from litigation or claims are disclosed in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
|
|
418: Customer Privacy
Topic-specific Standards |
Link |
Comment |
Global Compact Principles |
SDG |
|
418-1 |
Substantiated complaints concerning breaches of customer privacy and losses of customer data |
Sustainability Along the Value Chain: Emergency response, Corporate and Cyber Security |
As part of the implementation of its corporate strategy, BASF established a central governance, risk management and compliance unit at the beginning of 2020, which is responsible for topics such as cybersecurity. At an implementation level, BASF has an ISO/IEC 27001-certified information security management system (ISMS) steered by the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), who is operationally responsible for cybersecurity Group-wide. With respect to theft and loss of customer data: BASF has established risk management processes in place, combined with physical security and the implementation of technical and organizational controls on end devices and applications (e.g. encryption, data leakage prevention). No incidents within the meaning of GRI 418-1 were identified in 2022 (2021: 0). |
|
16 |